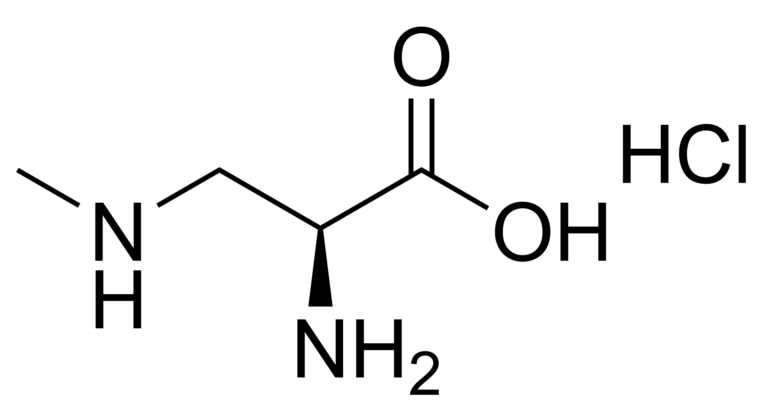
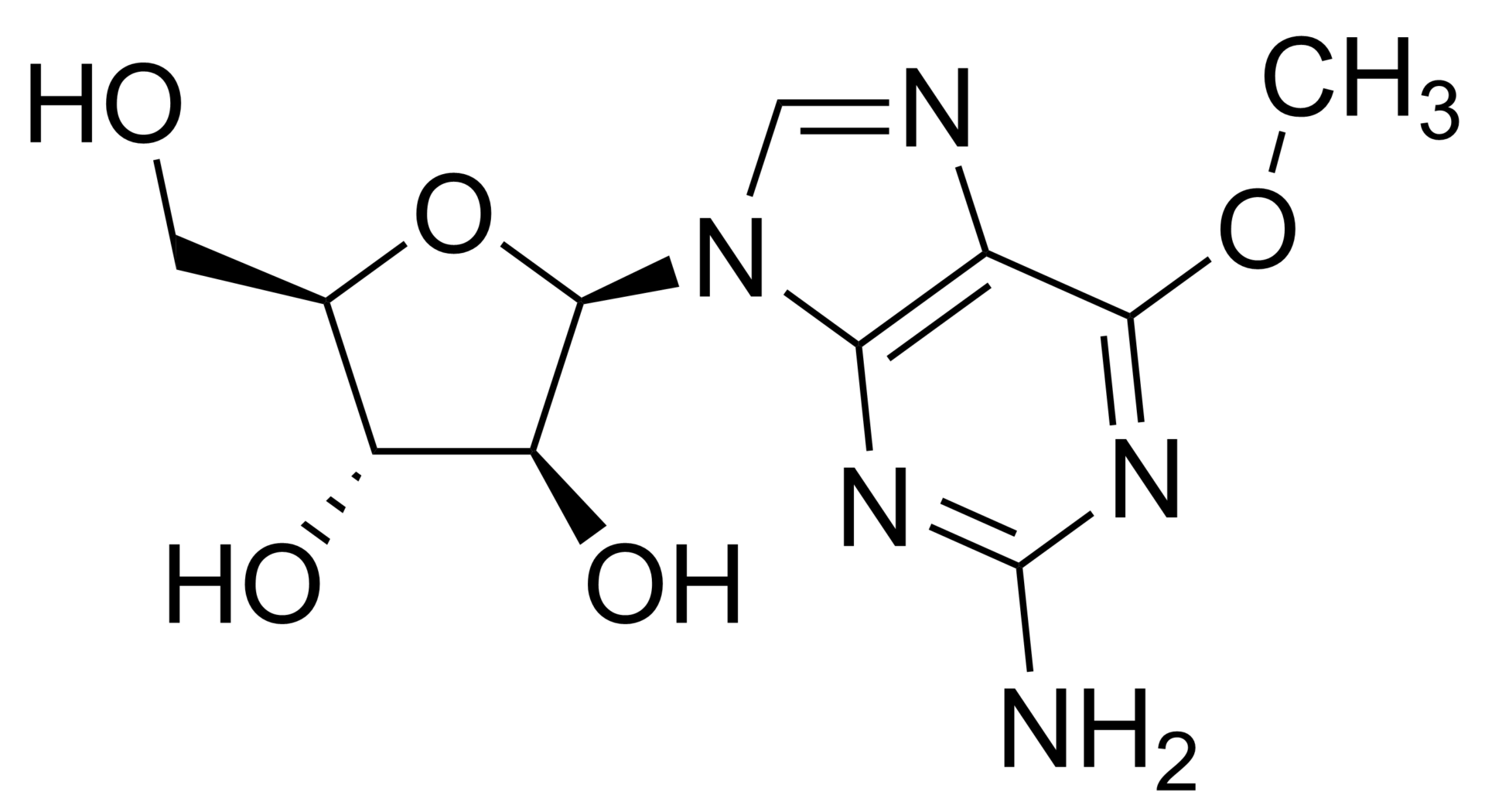
L-BMAA hydrochloride- CAS 16012-55-8
L-BMAA hydrochloride- CAS 16012-55-8 is distributed by Sigut Labs (Prague, Czech Republic)
Purity (LC-MS)
95 %
Package contents
L-BMAA hydrochloride
This compound is for research use only. We do not sell to patients.
| 1 g | € 1500 | Stock | ||
| 5 g | € 2600 | Stock | ||
| Do you want custom amount? | Custom amount | |||
Stock
Stock
Characterisation
Description
β-Methylamino-L-alanine/L-BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria.
BMAA is a neurotoxin and its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders (such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-Parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam, Guam ALS-PD) is the subject of scientific research. BMAA can cross the blood–brain barrier in rats. It takes longer to get into the brain than into other organs, but once there, it is trapped in proteins, forming a reservoir for slow release over time.
A study performed in 2015 with Vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus sabaeus) in St. Kitts, which are homozygous for the apoE4 gene (a condition which in humans is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease), found that vervets that were administered BMAA orally developed hallmark histopathology features of Alzheimer’s disease, including amyloid beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangle accumulation.
This product is distributed by Sigut Labs (Prague, Czech Republic).
Chemicals are distributed worldwide
Buy L-BMAA hydrochloride now, get your order in 48 hours.
- Shipping through DHL in 48 hours
- All compounds are safely and rigorously packed
Payment
- We are sending the invoice the same day as the shipment
- We are able to modify the invoice for the academic institution, so the order can be paid from grants
References
- SEAWRIGHT, A. A., Brown, A. W., Nolan, C. C., & Cavanagh, J. B. (1990). Selective degeneration of cerebellar cortical neurons caused by cycad neurotoxin, L‐β‐methylaminoalanine (L‐BMAA), in rats. Neuropathology and applied neurobiology, 16(2), 153-169.
- Tedeschi, V., Petrozziello, T., Sisalli, M. J., Boscia, F., Canzoniero, L. M. T., & Secondo, A. (2019). The activation of Mucolipin TRP channel 1 (TRPML1) protects motor neurons from L-BMAA neurotoxicity by promoting autophagic clearance. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 10743.
- Okle, O., Stemmer, K., Deschl, U., & Dietrich, D. R. (2013). L-BMAA induced ER stress and enhanced caspase 12 cleavage in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells at low nonexcitotoxic concentrations. toxicological sciences, 131(1), 217-224.
Similar products
Didn't find the chemical you were looking for?
Contact us
WHY CHOOSE
SigutLabs
Your impossible is our starting line
Partners & distributors