Overcoming challenges of lincomycin derivative scale-up
The process of scaling up is always very challenging. While sometimes products can be easily purified through methods like extraction or recrystallization, in certain cases, intermediates present a unique set of obstacles. Such was the scenario in this case where most of the intermediates were rich oily mixtures for which all the attempts of recrystallization failed.
Identifying the issue
SigutLabs undertook the scale-up synthesis of a highly active clindamycin derivative for the Institute of Microbiology of the Czech Academy of Science (Figure 1).
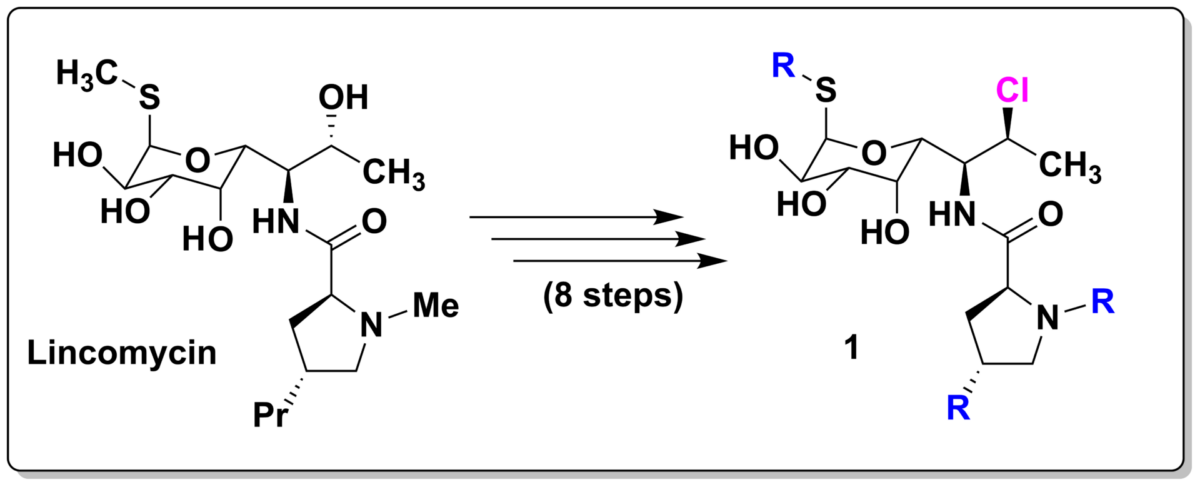
The given synthetic procedure was only designed for a small scale (100 mg) and contained several hidden issues. An illustrative example was the selective oxidation of -SMe moiety to sulfoxide with m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA). According to the given procedure, only 1 eq. of mCPBA was used even though the oxidation of amine nitrogen in the proline part of the lincomycin was also possible. This expected oxidation might significantly decrease the overall yield of the whole synthesis during scale-up.
Methodology insight
To address this challenge, we devised an alternative approach consisting of mild overoxidation to sulfoxide-N-oxide followed by the selective reduction of N‑oxide with sulfoxide moiety preservation. This action reduced the significant mass losses. Analyzing the intermediates posed another challenge, as the given procedure only utilized TLC for analysis, leaving a lack of information regarding the mixture composition. Moreover, HPLC and a similar method based on light absorption could not be used due to the very low absorption of the intermediates. However, we successfully overcame this challenge by the use of LC/MS as a convenient method for characterizing the crude reaction mixtures (Figure 2).

The last step of the synthesis, the selective chlorination of the secondary hydroxyl group, proved to be even more challenging. The lincomycin derivative molecule contains four secondary hydroxyl moieties which can be subsequently replaced by chlorine atoms. The frequently used chlorination agents (SOCl2, POCl3, PPh3 + NCS, PPh3 + CCl4,…) lead ultimately to overchlorination or undesired elimination of HCl from the molecule. Finally, we identified a mixture of DMF and (COCl)2 to serve our purpose as a very mild chlorination reagent.
Positive outcome
Using these reaction conditions, only traces of overchlorination were observed and ubiquitous elimination was negligible. The final purification process, conducted via reverse column chromatography on multigram scales, yielded the target product with purity exceeding 90 % (Figure 3).

In summary, through our optimized procedure, we successfully prepared more than 30 g of the desired lincomycin derivatives with excellent purity.
"Our molecule is now in the preclinical phase thanks to scale up done by the SigutLabs team."
Dr. Jiří Janata, Institute of Microbiology of the Czech Academy of Sciences


OUR CASE STUDY
Scale-up to accelerate drug discovery
Our experience helped overcome development hurdles for potential cancer & mental health drugs.
Read moreEmpowering neuro research with pro-N6pA
Sigut Labs scaled up pro-N6pA production, simplifying AMPylation research & boosting accessibility.
Read moreADC development leaps with new linkers
Novel linker design expedited ADC advancement, leading to promising lead compounds faster.
Read moreLincomycin derivative scale-up
Over 30 g of the desired product with exceptional purity was obtained through our optimized procedure.
Read morePurifying 350 kg of vitamin K2 oil
Our innovative scale-up technology helped to reduce the client’s purification process from days to hours.
Read more
Custom synthesis
Providing for a custom synthesis of previously reported molecules using described synthetic procedures.

Contract research
Developing novel synthetic routes to provide undescribed compounds in organic, bioorganic, and medicinal chemistry.

Scale-Up
Helping you go from lab scales to an industrial scale by applying our cutting-edge instrumentation.

Our Experts


Partners & distributors










